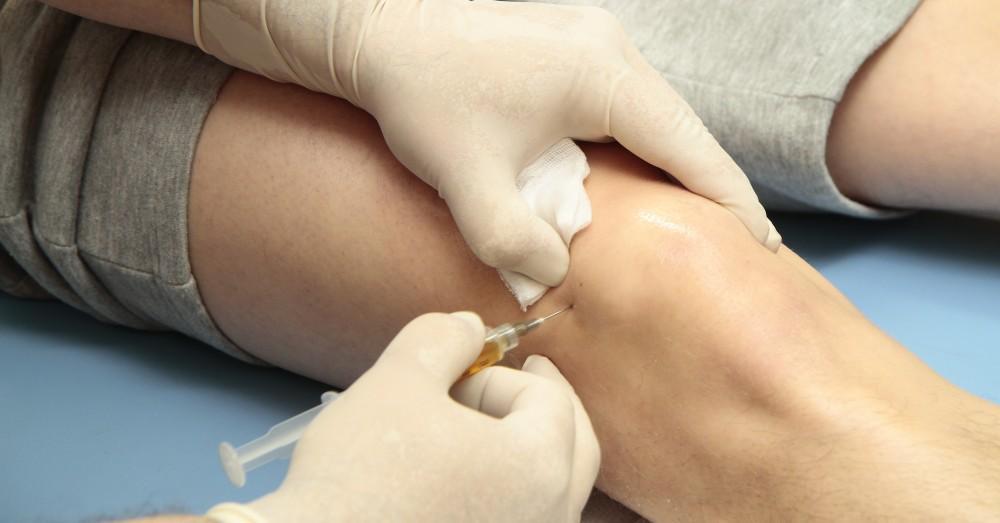
Interventional techniques can offer significant relief for knee pain, particularly when conservative treatments are insufficient. Here are some common interventional approaches for managing knee pain rehabilitation:
1. Corticosteroid Injections:
- Purpose: Reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from pain.
- How It Works: A corticosteroid medication is injected directly into the knee joint. The effects can last from a few weeks to several months.
2. Hyaluronic Acid Injections:
- Purpose: Lubricate the knee joint and improve mobility.
- How It Works: Hyaluronic acid is injected into the knee to mimic the natural joint fluid, which helps reduce pain and improve joint function. It’s often used for osteoarthritis.
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
- Purpose: Promote healing and reduce inflammation.
- How It Works: Blood is drawn from your body, processed to concentrate platelets, and then injected into the knee joint. PRP contains growth factors that may help repair damaged tissues.
4. Nerve Blocks:
- Purpose: Provide temporary pain relief by blocking pain signals.
- How It Works: An anesthetic or steroid is injected near the nerves that supply the knee joint, reducing pain for a period of time.
5. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA):
- Purpose: Provide long-term pain relief by disrupting nerve function.
- How It Works: Radiofrequency energy is used to heat and destroy nerve tissue that transmits pain signals, providing longer-lasting pain relief.
6. Synovial Fluid Analysis:
- Purpose: Diagnose and manage knee joint conditions.
- How It Works: A sample of the synovial fluid from the knee is taken and analyzed. This can help determine the cause of pain and guide treatment options.
7. Arthroscopic Surgery:
- Purpose: Diagnose and treat joint issues with minimal invasiveness.
- How It Works: A small camera (arthroscope) is inserted into the knee joint through a tiny incision. The surgeon can visualize and address issues such as torn cartilage or inflamed tissue.
8. Osteotomy:
- Purpose: Realign the knee joint to reduce pain and improve function.
- How It Works: Surgical procedure that involves cutting and repositioning the bone to relieve pressure on the affected area of the knee.
9. Meniscal Repair:
- Purpose: Repair a damaged meniscus.
- How It Works: Surgical procedure to mend a torn meniscus, which can help relieve pain and restore knee function.
10. Bursal Injection:
- Purpose: Reduce inflammation in the bursae (fluid-filled sacs) around the knee.
- How It Works: A corticosteroid or anesthetic is injected into the bursa to alleviate pain and swelling.
Considerations:
- Consultation: It’s essential to consult with an orthopedic specialist or pain management expert to determine the most appropriate interventional technique based on the specific cause of knee pain and overall health.
- Recovery and Risks: Each technique has its own recovery time and potential risks, which should be discussed with your healthcare provider.
These interventional techniques can provide significant relief and improve quality of life for individuals with knee pain, particularly when other treatments have not been effective.